Crm Software Pricing Comparison: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the world of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software can feel overwhelming, especially when faced with the diverse pricing models and feature sets available. This comprehensive guide cuts through the complexity, providing a clear and concise comparison of leading CRM software options and their associated costs.
We’ll explore various pricing structures, key features, and crucial factors to consider when selecting a CRM system that aligns perfectly with your business needs and budget.
From subscription-based plans to tiered pricing and freemium models, understanding the nuances of CRM pricing is paramount to making an informed decision. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to effectively evaluate different vendors, negotiate favorable terms, and ultimately optimize your investment in CRM technology.
We’ll examine real-world examples and offer practical tips to ensure you choose the solution that delivers the best return on investment.
Introduction
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software is a technology designed to manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. Its core functionalities include contact management, sales automation, marketing automation, customer service support, and reporting and analytics. Effectively utilizing CRM software allows businesses to improve customer relationships, streamline processes, and ultimately boost profitability.CRM software pricing is diverse and depends heavily on several factors.
Understanding these models is crucial for businesses seeking to implement a suitable system.
CRM Software Pricing Models
Different vendors employ various pricing strategies to cater to different business needs and sizes. A common model is subscription-based pricing, where users pay a recurring fee for access to the software, often monthly or annually. This fee can vary based on the number of users, features included, and level of support provided.
Tiered pricing structures offer various packages with escalating features and costs. A basic package might include essential functionalities, while premium packages unlock advanced capabilities like advanced analytics or integrations with other software. The freemium model provides a basic version of the software for free, with paid upgrades available for enhanced functionality.
Finally, some vendors offer perpetual licensing, a one-time purchase that grants permanent access to the software, although this model is less prevalent in the modern CRM market.
Factors Influencing CRM Software Pricing
Several key factors contribute to the final cost of CRM software. The number of users directly impacts pricing, as more users require more licenses. The specific features and functionalities required also play a crucial role; advanced features like AI-powered predictive analytics or robust integration capabilities command higher prices.
The level of support offered, ranging from basic email support to dedicated account managers, affects the overall cost. Customization requirements, including bespoke integrations or tailored workflows, can significantly increase the price. Finally, the vendor’s brand recognition and market position can also influence pricing, with established players often charging a premium.
For example, a small business might opt for a basic, affordable tiered package from a less established vendor, while a large enterprise might invest in a fully customized solution from a major player like Salesforce, accepting the higher associated costs.
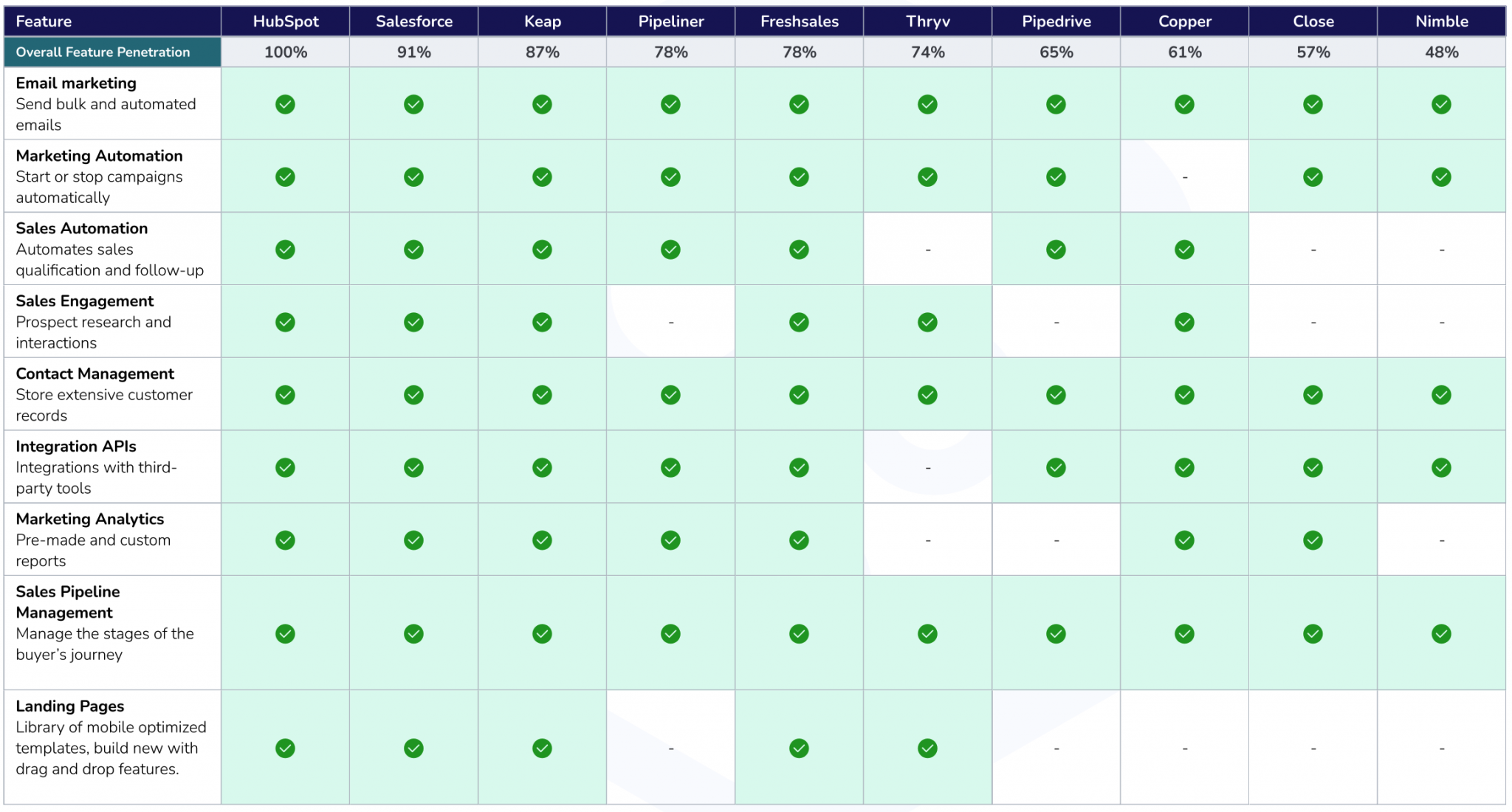
Key Features and Functionality Comparison
Choosing the right CRM often hinges on understanding the core features and how they differ across platforms and pricing tiers. This section provides a comparative analysis of leading CRM solutions, highlighting key functionalities and explaining how pricing impacts access to these features.
We will examine several prominent CRMs, focusing on their core offerings and the value proposition at each price point.
Core Feature Comparison Across Leading CRM Platforms
The following table compares the core functionalities of several popular CRM platforms. Note that feature availability and depth can vary significantly based on the chosen pricing tier.
| Feature | Salesforce Sales Cloud | HubSpot CRM | Microsoft Dynamics 365 | Zoho CRM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Management | Comprehensive contact database, custom fields, segmentation, and integration with other Salesforce tools. | Robust contact management with features for organization, tracking interactions, and email marketing integration. | Powerful contact management with advanced features like lead scoring and relationship mapping. | Extensive contact management capabilities, including custom fields, workflows, and integrations with other Zoho apps. |
| Sales Automation | Advanced sales automation with features like opportunity management, forecasting, and sales process automation. | Streamlined sales processes with tools for deal tracking, pipeline management, and email sequencing. | Robust sales automation tools, including lead routing, opportunity management, and sales performance analytics. | Sales automation features include lead management, opportunity tracking, and sales process automation. |
| Marketing Automation | Sophisticated marketing automation capabilities, including email marketing, campaign management, and lead nurturing. (Often requires additional Marketing Cloud license) | Built-in marketing automation tools for email marketing, social media management, and lead nurturing. | Marketing automation features are available through integration with Microsoft Dynamics 365 Marketing. | Comprehensive marketing automation features, including email marketing, social media management, and campaign tracking. |
| Reporting and Analytics | Highly customizable reporting and analytics dashboards, providing deep insights into sales performance and customer behavior. | User-friendly reporting and analytics dashboards, offering insights into key metrics such as website traffic, lead generation, and sales performance. | Powerful reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing for detailed analysis of sales data, customer interactions, and marketing campaigns. | Robust reporting and analytics features, offering customizable dashboards and reports to track key performance indicators. |
| Customer Service Tools | Comprehensive customer service tools, including case management, knowledge base, and service automation. (Often requires additional Service Cloud license) | Integrated customer service features, including ticketing systems, live chat, and email support. | Advanced customer service features, including case management, knowledge base, and service level agreement (SLA) management. | Customer service features include ticketing systems, email support, and self-service portals. |
Functionality Differences Across Pricing Tiers
Different pricing tiers within a single CRM platform often provide varying levels of access to features. For example, Salesforce Sales Cloud’s Essentials edition offers basic contact management and sales automation, while the Enterprise edition unlocks advanced features like forecasting, territory management, and custom application development.
Similarly, HubSpot’s free CRM provides core functionalities, while their paid tiers add features like marketing automation, sales automation tools, and advanced reporting. Zoho CRM follows a similar model, with its higher-tier plans offering more users, storage, and advanced features.
The added features in higher tiers often justify the increased cost by improving efficiency, providing more comprehensive data analysis, and supporting more complex business processes.
Features Justifying Higher Price Points
Higher price points in CRM solutions often reflect the inclusion of advanced features and capabilities. These may include:* Advanced analytics and reporting:Higher-tier plans often provide more sophisticated reporting and analytics tools, enabling deeper insights into customer behavior and sales performance. For example, predictive analytics capabilities, which forecast future sales trends based on historical data, are usually reserved for premium plans.
Extensive customization options
The ability to tailor the CRM to specific business needs through custom fields, workflows, and integrations is a significant differentiator, often found in more expensive plans.
Enhanced security and compliance
Higher-tier plans typically offer enhanced security features and compliance certifications, ensuring data protection and meeting industry regulations.
Dedicated support and onboarding
Premium plans often include dedicated customer support and comprehensive onboarding services, ensuring a smoother implementation and ongoing assistance.
Scalability and integration capabilities
Higher-tier plans usually offer greater scalability to accommodate business growth and extensive integration capabilities with other business applications. For example, seamless integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems or other specialized software is a common feature of premium CRM plans.
Pricing Structures and Cost Breakdown
Understanding the pricing models of different CRM systems is crucial for selecting a solution that aligns with your budget and business needs. This section details the pricing structures of several major CRM vendors, compares their total cost of ownership, and explores the impact of add-ons and integrations.
We’ll focus on providing a clear picture of what you can expect to pay.
Different CRM providers offer various pricing tiers, each catering to different business sizes and functionalities. These tiers typically range from basic plans suitable for small businesses to enterprise-level solutions packed with features and support for large organizations. The pricing model itself can also vary, from per-user subscriptions to tiered pricing based on features and data storage.
CRM Pricing Tiers: Examples from Major Vendors
The following examples illustrate the pricing structures of three prominent CRM vendors. Note that pricing is subject to change and can vary based on specific features, contract length, and other factors. It’s always recommended to check directly with the vendor for the most up-to-date information.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud:Salesforce offers a tiered pricing structure. Their Essentials plan might start around $25 per user per month, offering basic sales functionalities. Their Professional plan, costing more (e.g., around $75 per user per month), adds features like advanced reporting and analytics.
Their Enterprise and Unlimited plans offer even more features and support for larger organizations, with prices scaling accordingly.
- HubSpot CRM:HubSpot offers a freemium model, with a free version offering basic CRM functionalities. Their paid plans, such as the Starter, Professional, and Enterprise plans, offer progressively more advanced features and capabilities. The pricing typically increases based on the number of users and the features included.
For example, the Starter plan might start at a lower cost per month, while the Enterprise plan caters to larger businesses with more extensive needs and a higher price tag.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365:Microsoft Dynamics 365 offers various plans depending on the modules chosen (Sales, Customer Service, Marketing, etc.). Pricing is often quoted per user per month and varies significantly based on the specific modules and features selected. For instance, a basic Sales plan might start around $65 per user per month, while more comprehensive packages with multiple modules will increase the monthly cost.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Comparison
The total cost of ownership extends beyond the subscription fees. It includes implementation costs, training for users, ongoing support and maintenance, and potential customization expenses. These factors can significantly influence the overall cost of a CRM solution.
For example, implementing a complex CRM system like Salesforce Enterprise can involve substantial upfront costs for consultants, data migration, and system integration. Training users to effectively utilize the system also adds to the expense. Ongoing support, including technical assistance and updates, is an ongoing cost that must be factored in.
Smaller, simpler systems like HubSpot’s Starter plan might have lower implementation and training costs, but may require more manual work and lack the advanced support features of enterprise solutions.
Impact of Add-ons and Integrations
Many CRM systems offer add-ons and integrations that extend their functionality. These additions can range from marketing automation tools to e-commerce integrations. While these additions enhance the system’s capabilities, they also increase the overall cost. It’s important to carefully consider the necessary integrations and add-ons during the selection process and factor their cost into the budget.
For instance, integrating a marketing automation platform with a CRM system might require additional monthly fees or a one-time setup cost. Similarly, custom integrations with existing business systems can add to the overall cost of implementation and maintenance. A thorough assessment of required integrations and add-ons is essential to avoid unexpected expenses.
Factors Influencing CRM Software Selection
Choosing the right CRM software is a critical decision for any business, regardless of size. The ideal system must align seamlessly with your specific operational needs, budget constraints, and long-term growth strategy. A poorly chosen system can lead to wasted resources, decreased efficiency, and ultimately, hinder business success.
Careful consideration of several key factors is essential to ensure a positive return on investment.Selecting the appropriate CRM system requires a comprehensive evaluation of your business needs and available resources. This involves considering not only the software’s features but also its long-term implications for your operations and budget.
Ignoring these factors can lead to a costly mistake, impacting productivity and overall business performance.
Business Needs and Objectives
Understanding your business’s specific requirements is paramount. A small startup will have vastly different needs compared to a large enterprise. Consider the size of your sales team, the complexity of your sales process, your customer service strategies, and the overall volume of data you need to manage.
For instance, a small business focused on direct sales might require a simpler system with basic contact management and sales tracking capabilities, while a large enterprise with multiple sales channels and a complex product line would need a more robust and scalable solution with advanced analytics and reporting features.
Defining these needs clearly will guide you towards a CRM system that provides the necessary functionality without unnecessary complexity or cost.
Budget and Return on Investment (ROI)
Budgetary constraints are a significant factor in CRM selection. The cost of CRM software varies widely, encompassing licensing fees, implementation costs, training expenses, and ongoing maintenance. To evaluate ROI, businesses should consider factors like increased sales efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, reduced operational costs, and enhanced data-driven decision-making.
For example, a company might calculate ROI by comparing the increased revenue generated through improved sales processes with the total cost of implementing and maintaining the CRM system. A well-chosen CRM system should demonstrably improve efficiency and productivity, ultimately justifying the investment.
Consider developing a detailed cost-benefit analysis that includes both tangible and intangible benefits.
Scalability and Future Growth
Choosing a CRM system that can scale with your business is crucial for long-term success. Your needs will likely evolve as your business grows, so selecting a system that can adapt to increased user numbers, data volume, and more complex functionalities is essential.
For instance, a cloud-based CRM offers greater scalability compared to an on-premise solution, allowing for easier expansion and upgrades as your business grows. Consider your projected growth rate and choose a system that can accommodate this growth without requiring significant and costly upgrades or migrations in the near future.
Vendor Evaluation and Selection
Before committing to a purchase, thoroughly evaluate potential vendors. Consider their reputation, customer support capabilities, integration options with existing systems, and the overall ease of use of their software. Ask about implementation timelines, training resources, and ongoing maintenance support.
Choosing a reputable vendor with a proven track record and a strong commitment to customer support is critical for a successful CRM implementation. A strong vendor relationship will ensure smooth operation and access to timely assistance when needed.
Questions to Ask CRM Vendors
A structured approach to vendor selection is vital. Businesses should ask vendors about their experience with similar businesses, their implementation methodology, their customer support services, data security protocols, and their pricing models. It is also important to clarify the vendor’s commitment to ongoing system updates and enhancements to ensure the software remains current and effective.
Requesting case studies and references from existing clients can provide valuable insights into the vendor’s performance and the system’s effectiveness in real-world scenarios. Thorough due diligence will minimize the risk of choosing an unsuitable CRM system.
Case Studies
This section presents three hypothetical case studies illustrating how different businesses, with varying needs and budgets, chose suitable CRM software. Each case study details the selected software, its pricing, justification for selection, benefits, and potential drawbacks. This provides a practical understanding of CRM software selection in real-world scenarios.
Case Study 1: Small Startup
“GreenThumb Gardening”
“GreenThumb Gardening”
GreenThumb Gardening, a newly established landscaping company with five employees, requires a simple CRM to manage client contacts, projects, and scheduling. Their budget is limited to $50 per month. They chose HubSpot CRM’s free plan.HubSpot CRM’s free plan offers contact management, deal tracking, and basic reporting, perfectly aligning with GreenThumb’s needs.
The free plan’s limitations include restricted user access and limited automation capabilities.The benefits include cost-effectiveness and ease of use. The potential drawbacks are scalability issues as the company grows and limited advanced features compared to paid plans. The lack of robust automation may necessitate more manual data entry.
Case Study 2: Medium-Sized Business
“Artisan Coffee Roasters”
“Artisan Coffee Roasters”
Artisan Coffee Roasters, a growing coffee roaster with 20 employees, needs a CRM to manage customer relationships, track sales, and analyze customer preferences for targeted marketing campaigns. Their budget is $500 per month. They selected Zoho CRM’s Professional plan.Zoho CRM’s Professional plan provides features like advanced reporting, workflow automation, and sales pipeline management, catering to Artisan Coffee Roasters’ growth needs.
The monthly cost is justified by the increased efficiency and improved customer insights provided.The benefits include enhanced sales tracking, automated marketing campaigns, and better customer segmentation. Potential drawbacks include a steeper learning curve compared to simpler CRMs and the need for additional training for employees.
The range of features may also include some that are unused by the company, representing a small level of cost inefficiency.
Case Study 3: Large Enterprise
“GlobalTech Solutions”
“GlobalTech Solutions”
GlobalTech Solutions, a large multinational technology company with over 500 employees, requires a sophisticated CRM to manage customer interactions across multiple departments and geographical locations. Their budget is flexible but prioritizes a robust, scalable solution. They chose Salesforce Sales Cloud’s Enterprise Edition.Salesforce Sales Cloud’s Enterprise Edition offers comprehensive features including advanced analytics, customizable dashboards, and integration capabilities with other enterprise applications.
The high cost is justified by the scalability, customization options, and enhanced data security required for a large multinational corporation.The benefits include seamless integration across departments, improved data visibility, and enhanced customer service capabilities. Potential drawbacks include the high initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs, the complexity of the system requiring specialized training, and the need for ongoing IT support.
Customization can also become very complex and costly over time.
Tips for Negotiating CRM Software Pricing
Negotiating the price of CRM software can significantly impact your budget and overall ROI. A strategic approach, combining thorough preparation with skillful negotiation tactics, can secure favorable terms and ensure you’re getting the best value for your investment. This section Artikels key strategies to help you navigate the pricing discussion effectively.Effective negotiation hinges on a clear understanding of your needs and the vendor’s pricing model.
Before entering price discussions, you should have a firm grasp of your requirements, budget constraints, and the competitive landscape. This allows you to approach negotiations from a position of strength and confidently advocate for the best possible price.
Leveraging Competitive Pricing Information
Competitive pricing intelligence is a powerful tool in price negotiations. Researching competitor offerings and their pricing structures allows you to establish a benchmark and justify your desired price point. For example, if a competitor offers a similar solution at a lower cost, you can use this information to negotiate a comparable price with your chosen vendor.
Presenting this data in a professional and factual manner, without being confrontational, can be highly effective. Remember to compare apples to apples; ensure you are comparing features and functionalities of equivalent value when assessing competitive pricing.
Clearly Defining Needs and Requirements
Before initiating price discussions, thoroughly define your business needs and requirements. This involves identifying specific functionalities, user numbers, integration needs, and expected support levels. A detailed requirements document will not only guide your software selection but also serve as a strong basis for negotiating price.
For instance, if you only require basic functionalities, you can leverage this to negotiate a lower price for a less comprehensive package, rather than paying for features you won’t utilize. This process ensures you are only paying for what you need, avoiding unnecessary expenses.
Negotiating Contract Terms and Conditions
Beyond the initial price, pay close attention to the contract’s terms and conditions. Negotiate favorable payment terms, such as staggered payments or discounts for upfront payments. Explore options for contract length, ensuring flexibility for your business’s evolving needs.
For example, negotiating a shorter contract term can provide more flexibility if your requirements change or if a better offer emerges in the future. Furthermore, carefully review clauses related to upgrades, maintenance, and support to avoid hidden costs down the line.
Understanding these aspects is crucial for optimizing your overall investment.
Exploring Alternative Pricing Models
Many CRM vendors offer various pricing models, such as subscription-based, per-user, or tiered pricing. Explore these options and identify the model that best aligns with your budget and usage patterns. For example, a per-user model might be more cost-effective if you have a small team, while a tiered model allows you to scale up or down based on your needs.
By understanding these different options, you can make a more informed decision and potentially negotiate a more favorable arrangement. Remember to compare the total cost of ownership across different pricing models before making a final decision.
Future Trends in CRM Software Pricing
The pricing landscape for CRM software is in constant flux, driven by technological advancements and evolving business needs. We can expect significant shifts in the coming years, influenced by factors such as artificial intelligence, the increasing sophistication of CRM functionalities, and the growing preference for flexible subscription models.
Understanding these trends is crucial for businesses to effectively budget and strategize their CRM investments.The integration of AI and machine learning into CRM platforms is poised to revolutionize pricing strategies. AI-driven pricing models will allow for greater granularity and personalization, moving away from one-size-fits-all pricing plans.
This will likely manifest in dynamic pricing based on usage, user profiles, and even predicted future needs, leading to more tailored and potentially more cost-effective solutions for specific business contexts. For example, a small business might pay a lower monthly fee for basic features and limited user access, while a large enterprise with complex needs and a vast user base would pay a higher premium for advanced functionalities and extensive support.
AI-Driven Pricing and Subscription Model Variations
AI will play a significant role in optimizing CRM pricing. Predictive analytics can forecast a customer’s future needs and adjust pricing accordingly. This allows for a more flexible approach, offering customized pricing plans that reflect individual business requirements and usage patterns.
Subscription models will become increasingly nuanced, offering tiered pricing with add-on modules for specialized features. Businesses might choose a core subscription and add-on features like advanced analytics, e-commerce integration, or specific industry-focused functionalities, paying only for what they actually need.
This contrasts with traditional, fixed-price licensing models which often leave businesses paying for unused features. Companies like Salesforce already offer a wide variety of subscription tiers and add-ons, demonstrating this trend’s current momentum.
Value-Based Pricing and Outcome-Oriented Models
A shift towards value-based pricing is anticipated. Instead of focusing solely on features, providers will increasingly emphasize the value delivered to the customer. This means pricing models might be linked to demonstrable improvements in key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales conversion rates, customer retention, or operational efficiency.
Outcome-oriented pricing models, where the cost is tied to the achievement of specific business goals, are also likely to gain traction. For instance, a CRM provider might charge a percentage of revenue generated through leads acquired using their platform, incentivizing both the provider and the customer to achieve mutually beneficial results.
This model aligns the interests of the vendor and the customer, promoting a collaborative relationship focused on achieving measurable business outcomes.
The Outlook for CRM Software Pricing
In summary, the future of CRM software pricing points towards greater flexibility, personalization, and a stronger focus on value. AI-driven dynamic pricing, tiered subscription models, and outcome-oriented pricing will become increasingly prevalent, offering businesses more tailored and cost-effective solutions.
This shift requires businesses to carefully evaluate their needs, choose pricing models that align with their strategic goals, and actively negotiate with vendors to secure the best possible terms. The days of simple, fixed-price licensing models are likely numbered, replaced by a more sophisticated and dynamic pricing landscape.
Conclusion
Selecting the optimal CRM software involves careful consideration of numerous factors beyond just the initial price tag. This guide has provided a framework for a thorough evaluation, encompassing pricing structures, feature comparisons, and crucial decision-making considerations. By understanding the total cost of ownership, leveraging negotiation strategies, and focusing on ROI, businesses can confidently choose a CRM solution that not only meets their current needs but also scales effectively to support future growth.
Remember to prioritize features aligned with your specific business goals and don’t hesitate to engage with vendors to clarify any uncertainties before committing to a long-term investment.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the average cost of CRM software?
The cost varies greatly depending on the vendor, features, and number of users. Expect to see prices ranging from free (for limited functionality) to thousands of dollars per month for enterprise-level solutions.
Can I negotiate CRM software pricing?
Yes, negotiating is often possible, particularly for larger contracts or when comparing multiple vendors. Clearly defining your needs and leveraging competitive pricing information strengthens your negotiating position.
What are the hidden costs associated with CRM implementation?
Hidden costs can include data migration, customization, integration with existing systems, training for employees, and ongoing maintenance and support.
How long does it take to implement CRM software?
Implementation timelines vary depending on the complexity of the system and the size of your business. Expect a timeframe ranging from a few weeks to several months.